INTRODUCTION
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis (VRE), represent significant challenges to global public health due to their high rates of morbidity, mortality, and resistance to multiple antibiotics [1,2]. Both MRSA and VRE are major opportunistic pathogens and are responsible for nosocomial infections, particularly in immunocompromised patients [1,2]. MRSA was first described in 1961, while VRE emerged as a major clinical concern in 1980. They have become a cause of hospital-acquired infections all over the world, predominantly affecting patients undergoing invasive procedures or those with weakened immune systems [2–4].
The molecular mechanisms of MRSA and VRE resistances are different. MRSA resistance primarily links to the acquisition of the mecA gene, which encodes penicillin-binding protein 2a (PBP2a) [3,5]. This transpeptidase involves the biosynthesis of bacteria cell walls and shows a lower affinity of β-lactam antibiotics than the other PBPs [3,4]. In contrast, VRE resistance is primarily associated with the presence of the VanA ligase, encoded by the VanA gene. This enzyme alters the compositions of peptidoglycan synthesis, replacing the terminal D-alanine with D-lactate, thereby decreasing vancomycin binding [2,4,6].
Treating MRSA and VRE infections remains challenging due to the limitations of available antibiotics [2,5,7]. Strains of MRSA and VRE are resistant to a broad spectrum of antibiotics, including β-lactams, respiratory fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides, macrolides, and tetracyclines [2,7]. Vancomycin and daptomycin are typically used as first-line drugs for severe MRSA infection [8], while linezolid is commonly employed for VRE infection [9]. Unfortunately, these antibiotics are often associated with serious adverse effects, such as myelosuppression, nephrotoxicity, and peripheral neuropathy [10,11]. The prolonged use of linezolid in clinical settings has also contributed to the emergence of acquired resistance in MRSA [12]. Moreover, vancomycin has been reported to exhibit slower bacterial killing than β-lactams in clinical studies [13,14].
Combination therapy is increasingly recommended to minimize prolonged antibiotic use and reduce the risk of developing multidrug resistance [15–17]. There are recent studies suggesting that pure natural compounds and/or a combination of natural compounds and antibiotics to provide a promising solution to this growing problem of antibiotic resistance. Several chemical constituents of plants have shown antibacterial activity against a range of clinically significant pathogens, including Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Enterococcus faecalis [18,19]. Phytochemicals have the potential to enhance the efficacy of existing antibiotics, such as amoxicillin, gentamicin, teicoplanin, and daptomycin, particularly against MRSA and VRE [19–21]. For example, longistylin A, an isoprenylated stilbene isolated from the leaves of pigeon pea [Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp], exhibited strong antibacterial activity against MRSA and promoted wound healing in an MRSA-infected mouse model [21]. The trans-stilbenes such as pinosylvin monomethyl ether, piceatannol and resveratrol have demonstrated antibacterial activity against various pathogenic bacteria, including both Gram-negative (Salmonella enterica) and Gram-positive bacteria (Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and Staphylococcus aureus) [22]. Diosmetin, a flavonoid from aerial parts of Sophora moorcroftiana (Benth). Benth. ex Baker, showed a synergistic effect with antibiotics against the four S. aureus drug-resistant types (SA1199B, RN4220, EMRSA-15, and MRSA strains) [23,24]. Glycyrrhizic acid, a triterpene saponin from licorice root (Glycyrrhiza glabra L.), increased VRE growth inhibition when combined with gentamicin, teicoplanin, and daptomycin [20]. Piperine, an amide alkaloid from black pepper (Piper nigrum L.), showed antibacterial activity against Gram-positive (Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus) and Gram-negative bacteria (Escherichia coli) [25], and exhibited a synergistic effect with gentamicin in killing MRSA [26].
Previously, we isolated major compounds from the whole plants of Paphiopedilum dianthum Tang & F.T. Wang (Orchidaceae), yielded pinosylvin monomethyl ether (1), 2,3’-dihydroxy-5’-methoxystilbene (2), (E)-2,3′-dihydroxy-2′-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-5′-methoxystilbene (3), (E)-2,5′-dihydroxy-2′-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-3′-methoxystilbene (4), isalpinin (5), oleanolic acid 28-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (6) [25], and piperine (7) isolated from Piper wallichii (Miq.) Hand.-Mazz (Piperaceae) [27]. Some of them exhibited potential antibacterial effects against MRSA and VRE when combined with antibacterial drugs. Previous studies have shown that amoxicillin can be effective in combination with various compounds against MRSA and VRE, including cefdinir, light-activated methylene blue, and fosfomycin [15–17]. However, the studies on amoxicillin plus phytochemicals are a limited amount of additional research.
The aim of this study was to investigate the antibacterial activity of phytochemicals 1–7 (Fig. 1) against nosocomial MRSA and VRE. All compounds were evaluated both individual and in combination with amoxicillin. The molecular mechanisms underlying the antimicrobial activity of these combinations were explored. Antibacterial activity was evaluated using the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC). A checkerboard microdilution assay was performed to determine the fractional inhibitory concentration (FIC) index and to estimate potential synergistic effects. Additionally, computational molecular docking was conducted to explore the binding affinity and molecular interactions with resistance-targeted proteins: PBP2a for MRSA and VanA ligase for VRE.
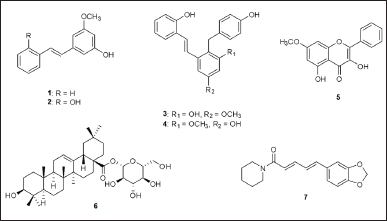 | Figure 1. Chemical structures of compounds 1–7. [Click here to view] |
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Chemicals and microorganisms
Mueller–Hinton broth was purchased from Himedia Company (Mumbai, India). Resazurin dye was obtained from Sigma Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA). Amoxicillin was purchased from Siam Pharmaceutical Company (Bangkok, Thailand). Dried roots and dried leaves of Paphiopedilum dianthum Tang & F.T. Wang and dried stems of Piper wallichii (Miq.) Hand.-Mazz were soaked in methanol and concentrated by rotary evaporator. Each of the methanol extracts was purified by column chromatography and identified pure compounds by spectroscopic methods together with a comparison of the spectral data with previous reports. Pinosylvin monomethyl ether, 2,3’-dihydroxy-5’-methoxystilbene, (E)-2,3’-dihydroxy-2’-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-5’-methoxystilbene, (E)-2,5’-dihydroxy-2’-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-3’-methoxystilbene, isalpinin and oleanolic acid 28-O-β-D-glucopyranoside were obtained from Paphiopedilum dianthum Tang and F.T. Wang [25], while piperine was yielded from Piper wallichii (Miq.) Hand.-Mazz [27].
The pathogenic MRSA and VRE strains used in this study were clinically isolated and obtained from the Faculty of Medical Technology, Rangsit University. These bacterial strains were collected from clinical specimens following standard microbiological procedures. Isolation was performed using selective and differential media, including Mannitol Salt Agar for MRSA and Bile Esculin Azide Agar supplemented with vancomycin for VRE, to ensure the accurate identification of resistant strains. The identification and confirmation of MRSA and VRE were confirmed by the disk diffusion method, according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines, and by determining the MIC using the broth microdilution method. The disk diffusion method was employed to estimate the resistance profiles against commonly used antibiotics, while MIC testing provided quantitative data on the resistance levels of MRSA and VRE strains [28].
Determination of the MIC
The MIC of seven phytochemicals and amoxicillin against MRSA and VRE strains was determined using the microdilution method, following the guidelines from the CLSI [29]. MRSA or VRE (5 × 106 CFU/ml) was inoculated into a 96-well plate containing two-fold serial dilutions of phytochemicals (0.02–10 mg/ml) or amoxicillin (0.02 to 10 mg/ml) in Mueller–Hinton broth. After 24 hours of incubation at 37°C, the viability of MRSA and VRE was measured by using a resazurin-based assay with the addition of resazurin dye (0.10% w/v) for another 2-hour incubation. A color change from blue to pink at the lowest concentration of all phytochemicals and amoxicillin was observed to interpret MIC in both MRSA and VRE strains.
Assessment of synergistic effect
The checkerboard microdilution method was used to assess the combined antibacterial effects of amoxicillin and seven phytochemicals [15,17]. The FIC index was calculated to quantify the synergistic effects between seven phytochemicals and amoxicillin against MRSA and VRE strains. MRSA or VRE (5 × 106 CFU/ml) was cultured in a 96-well plate in Mueller–Hinton broth, with amoxicillin at ½ of MIC and all phytochemicals at concentrations ranging from 0.01 to 10 mg/ml. In parallel, each natural compound was co-incubated at a concentration of ½ MIC with amoxicillin at concentrations ranging from 0.0001 to 10 mg/ml. The viability of MRSA and VRE strains was assessed using the same procedures as those used for MIC determination in susceptibility testing. The FIC index was calculated as follows: FICamoxicillin = MIC of amoxicillin in combination/MIC of amoxicillin alone, FICphytochemical = MIC of phytochemical compound in combination/MIC of phytochemical compound alone, and FIC index = FICamoxicillin+ FICphytochemical. Furthermore, FIC index values were interpreted as follows: <0.5 suggested synergy, 0.5–0.75 indicated partial synergy, 0.76–1 represented an additive effect, and >2 suggested antagonism [30].
Molecular docking studies
Molecular docking was used to investigate the ligand-protein interactions between proteins including PBP2a (PDB ID: 4cjn) from MRSA and VanA (PDB ID: 1e4e) from VRE and eight ligands [31–33]. Water molecules were removed from the PBP2a and VanA proteins, and hydrogen atoms were added. Gasteiger charges were assigned to both proteins using AutoDock Suite 4.2.6 (TSRI, La Jolla, CA, USA). The 3-D structures of the two proteins and the eight compounds were converted into PDBQT format files. A grid box with dimensions of 120 × 120 × 120 Å was set up for docking simulations. Flexible ligands were docked using the Lamarckian genetic algorithm with default parameters, repeated 10 times. The lowest binding free energy (ΔG) and inhibition constant (Ki) were recorded from the docking results. The top ligand-protein docking interactions were visualized in both 2-D and 3-D formats using Discovery Studio 2021 Client (BIOVIA, San Diego, CA, USA).
RESULTS
In vitro antibacterial activity
In vitro susceptibility testing revealed that all seven phytochemicals exhibited potential antibacterial effects against both MRSA and VRE strains after 24 hours of incubation (Table 1). Additionally, amoxicillin inhibited the growth of MRSA and VRE at a MIC of 0.125 mg/ml. Compounds 1–3 showed stronger MRSA growth inhibition (MIC = 5 mg/ml) than compounds 4–7 (MIC = 10 mg/ml). Moreover, compounds 3 and 4 also exhibited VRE growth inhibition, with the lowest MIC value of 5 mg/ml. Compounds 1, 2, 5, 6, and 7 inhibited VRE growth at an MIC of 10 mg/ml.
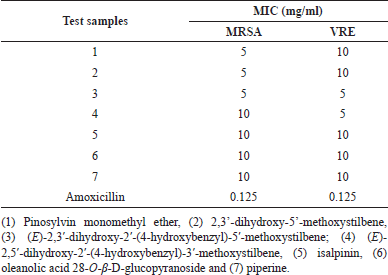 | Table 1. Minimum inhibitory concentration of test samples for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis. [Click here to view] |
Synergistic study
Synergistic testing was performed to evaluate the potentiation of compounds 1–7 in enhancing the antibacterial activity of amoxicillin against MRSA and VRE. For the inhibition of MRSA growth, all seven phytochemicals demonstrated FIC index values ranging from 0.8010 to 0.8020, indicating an additive enhancement of amoxicillin’s antibacterial activity against MRSA when combined with these compounds (Table 2). Remarkably, all compounds exhibited strong synergistic effects with amoxicillin against the VRE strain, as evidenced by low FIC index values. Compounds 1–2 showed the potent synergy with amoxicillin, resulting in an FIC index of 0.0018. Phytochemicals 3–4 also demonstrated strong synergy, with an FIC index of 0.0100. The remaining compounds 5–7 exhibited synergistic effects in amoxicillin-treated VRE, with an FIC index of 0.0810. These results suggest that the phytochemicals alone showed low to moderate potency against MRSA and VRE strains, they significantly enhanced the efficacy of amoxicillin when used in combination, particularly against VRE strain.
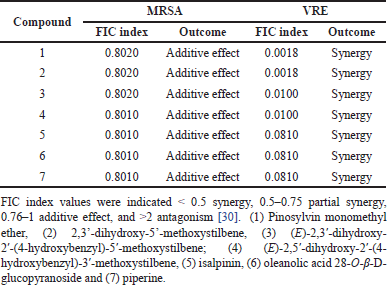 | Table 2. Fractional inhibitory concentration (FIC) index of test samples for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin resistant Enterococcus faecalis (VRE) in combination with amoxicillin. [Click here to view] |
Molecular docking of PBP2a in MRSA and VanA ligase in VRE
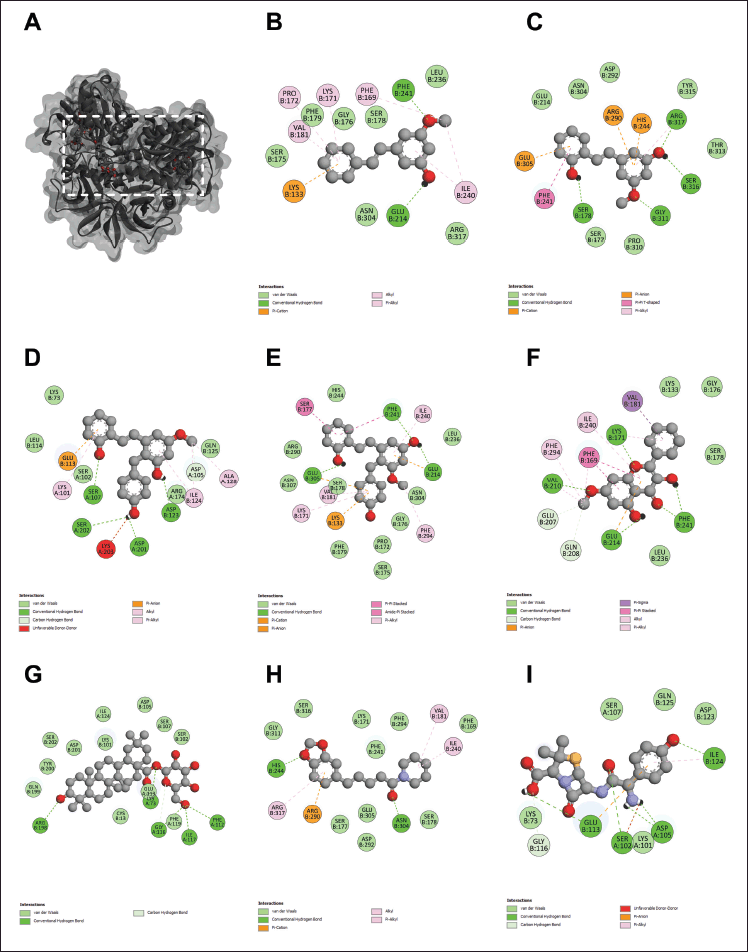
To elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying the synergistic effects of the combination of phytochemicals and amoxicillin against MRSA and VRE, molecular docking was performed on PBP2a for MRSA and VanA ligase for VRE, followed by an analysis of ΔG, Ki, and molecular interactions. As shown in Figure 2 and Table 3, the ΔG values of compound 1 (−6.60 kcal/mol), compound 2 (−6.82 kcal/mol), compound 3 (−7.48 kcal/mol), compound 4 (−8.25 kcal/mol), compound 5 (−7.69 kcal/mol), compound 6 (−11.70 kcal/mol), and compound 7 (−7.45 kcal/mol) indicated stronger binding affinity to PBP2a than amoxicillin (−6.41 kcal/mol). Correspondingly, all these phytochemicals showed lower Ki values than amoxicillin, by approximately 1.4–7650 folds. The top-ranked phytochemical was compound 6, which interacted remarkably with the residues ARG110, ASN111, LYS176, ASN177, ASP209, and PHE211 in the PBP2a binding pocket through conventional hydrogen bonds. Compounds 4 and 5 demonstrated the second and thirdhighest scores in the PBP2a binding pocket, respectively. They interacted with the residue LEU147, LYS148, and LYS318 via conventional hydrogen bonds, carbon-hydrogen bonds, alkyl-alkyl interactions, pi-alkyl interactions, or pi-sigma interactions, similar to compounds 1 and 7. Although compound 3 is an isomer of compound 4 by alternating substituent groups between hydroxyl and methoxy groups at 3′ and 5′, it bound to different amino residues forming conventional hydrogen bounds with ARG110 and ILE309, a carbon–hydrogen bond with PRO213, alkyl-alkyl interactions with TRP205 and PRO213, and a pi-sigma interaction at ALA310. One of the seven phytochemical compounds, compound 1 showed low-binding affinity for PBP2a. In contrast, amoxicillin showed negligible interaction with PBP2a compared to all tested compounds (Table 3).
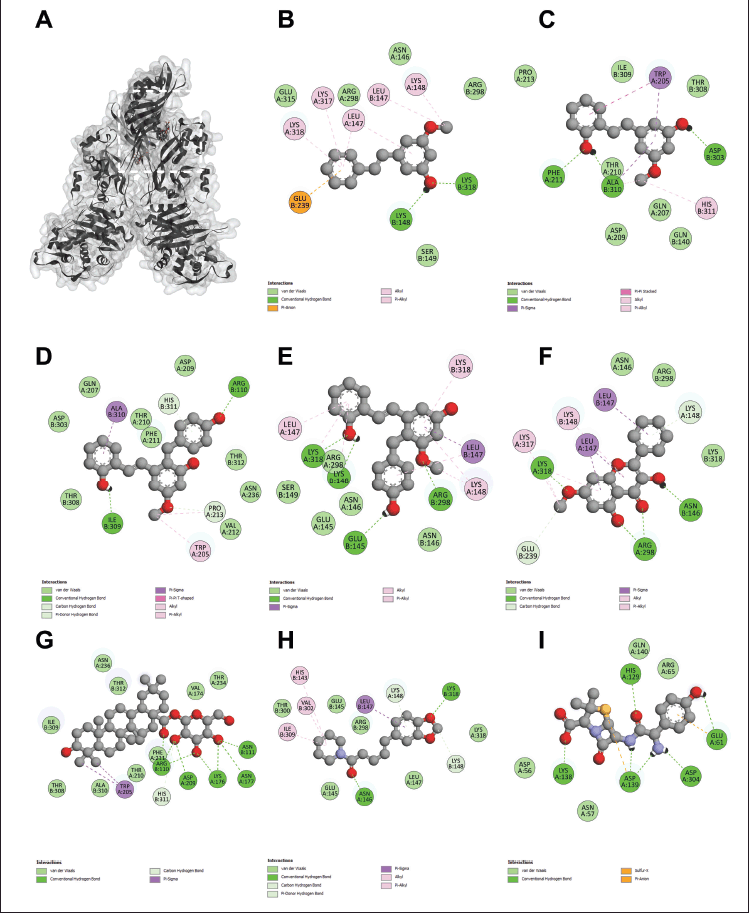 | Figure 2. The 3D interaction between test samples and penicillin binding protein 2a (PBP2a) in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) (A). The 2D molecular docking interactions of compound 1 (pinosylvin monomethyl ether, B), compound 2 (2,3’-dihydroxy-5’-methoxystilbene, C), compound 3 [(E)-2,3′-dihydroxy-2′-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-5′-methoxystilbene, D], compound 4 [(E)-2,5′-dihydroxy-2′-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-3′-methoxystilbene, E], compound 5 (isalpinin, F), compound 6 (oleanolic acid 28-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, G), compound 7 (piperine, H) and β-lactam amoxicillin (I) with PBP2a in MRSA. [Click here to view] |
 | Table 3. Molecular interaction between test samples and penicillin binding protein 2a (PBP2a) in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). [Click here to view] |
As shown in Figure 3 and Table 4, our study revealed that all compounds could bind to the VanA ligase in VRE with greater affinity than amoxicillin. The seven compounds achieved ΔG scores ranging from –10.46 to –7.08 kcal/mol, whereas amoxicillin had a ΔG score of –6.59 kcal/mol. Similarly, they displayed Ki values (0.021–5.32 µM) lower than the Ki value of amoxicillin (14.66 µM). Compound 6 exhibited excellent binding affinity to the VanA ligase in VRE by interacting with residues LYS73, PHE112, GLY116, ILE117, and ARG198 through conventional hydrogen and carbon–hydrogen bonds. Compounds 4 and 7 showed the second and third-highest affinities for the VanA ligase in VRE, respectively. They interacted with residue VAL181 and ILE240 via pi-alkyl interaction, similar to compounds 1 and 5. Compound 3 also interacted with different amino acid residues on VanA ligase in VRE, even though it contained the same core structure of compound 4, as shown in Figure 3 and Table 4. Moreover, amoxicillin interacted with the same amino acid residues (GLU113 and ILE124) on VanA ligase, which was similar to compound 3.
 | Figure 3. The 3D interaction between test compounds and VanA ligase enzyme in VRE (A). The 2D molecular docking interactions of compound 1 (pinosylvin monomethyl ether, B), compound 2 (2,3’-dihydroxy-5’-methoxystilbene, C), compound 3 [(E)-2,3′-dihydroxy-2′-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-5′-methoxystilbene, D], compound 4 [(E)-2,5′-dihydroxy-2′-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-3′-methoxystilbene, E], compound 5 (isalpinin, F), compound 6 (oleanolic acid 28-O-β-D-glucopyranoside, G), compound 7 (piperine, H) and β-lactam amoxicillin (I) with VanA in VRE. [Click here to view] |
 | Table 4. Molecular interaction between test compounds and VanA ligase enzyme in vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis (VRE). [Click here to view] |
DISCUSSION
Phytochemicals are produced by plants to protect from unsuitable conditions, such as pests and microorganisms. Vegetables, fruits, and herbs contain several phytochemicals, such as alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenoids, and stilbenoids to treat some infectious diseases. Thus, these compounds might show antimicrobial activity. Our study selected seven natural compounds from plants, including four stilbenoids (compounds 1–4), one flavonoid (compound 5), one triterpenoid saponin (compound 6), and one amide alkaloid (compound 7). All compounds were assessed in vitro and in silico antimicrobial effects against MRSA and VRE strains because they are responsible for severe infections in various human tissues, including the respiratory tract, skin and soft tissues, and bones and joints. Both strains pose significant health risks due to their ability to withstand multiple antibiotics [1–4]. In light of the increasing global health burden posed by antibiotic-resistant bacteria, it is imperative to explore alternative therapeutic strategies. Recent data emphasizes the urgency of addressing MRSA and VRE infections, which remain a significant clinical challenge despite advances in medical research [15–17]. Our study not only provides an in-depth analysis of the current state of research but also identifies key gaps in literature review, particularly the need for new treatment strategies.
Compounds 2–6 and the combination of β-lactam antibiotic amoxicillin and phytochemicals 1–7 were assessed in vitro and in silico antimicrobial effects against MRSA and VRE strains for the first time. Furthermore, they are underexplored but holds great potential for overcoming antibiotic resistance. All compounds could inhibit the growth of both MRSA and VRE in our results of susceptibility testing. Compound 3 exhibited the strongest antibacterial effect (MIC of 5 mg/ml) against both strains. Compounds 1 and 2 were effective against MRSA (MIC 5 mg/ml), while compound 4 was effective only against VRE (MIC 5 mg/ml). Compounds 5–7 showed a higher MIC of 10 mg/ml to inhibit both strains.
Previous studies indicated natural stilbenes, especially the oxygenated at positions 3 and 5 of stilbenes against MRSA strain. Chiricanine A is a prenylated stilbene derivative that is isolated from fungus-elicited peanuts. It showed the most potent with MIC of 12.5 μg/ml in MRSA when compared to stilbenes without prenylation, including piceatannol, pinosylvin, and resveratrol [34,35]. Longistylin A, is a 4-prenylated pinosylvin monomethyl ether purified from leaves of Cajanus cajan, which was strongly potent against MRSA with MIC of 1.56 μg/ml. It might act to disturb bacteria membranes leading to increased permeability of cells [35]. Stilbenoids 1–4 could also act as chiricanine A and longistylin A to reveal antimicrobial activity against MRSA. Furthermore, compounds 3–4 are the most potent to inhibit VRE growth with a MIC value of 5 mg/ml. Both of them contain 4-hydroxybenzyl substituent group which could be an essential part of action.
The results of this study each of the phytochemicals 1–7 exhibited varying levels of potency in inhibiting MRSA and VRE growth, they all exhibited synergistic effects when co-treated with the amoxicillin against for VRE and additive effect for MRSA. This effect was not dependent on the type or specific class of phytochemicals. The FIC index showed stronger synergy for VRE (FIC index: 0.0018–0.0810) than MRSA (FIC index: 0.8010–0.8020). This suggests that the degree of synergy between the compounds and amoxicillin depends on the specific bacterial strain and its resistance mechanisms, especially in MRSA and VRE.
The novelty of this study has not been extensively studied in previous contexts but it provides new insights by evaluating a broader range of compounds and analyzing their molecular interactions with key resistance mechanisms in MRSA and VRE. The molecular docking studies provide novel evidence that these compounds interact specifically with the allosteric domains of PBP2a and VanA ligase, contributing to the understanding of their potential mechanisms of action.
The upregulation of the mecA gene increases the production of PBP2a, which reduces the effectiveness of β-lactam antibiotics, contributing to antibiotic resistance [3,5]. β-lactam amoxicillin binds specifically to PBP1, PBP2, and PBP3 in Staphylococcus aureus [15]. Our results demonstrated that β-lactam amoxicillin had a weak binding affinity for PBP2a in MRSA, with ΔG: −6.41 kcal/mol and Ki: 20.12 µM, as shown by molecular docking studies. In contrast, all compounds exhibited strong interaction with PBP2a (ΔG: −11.7 to −6.60 kcal/mol; Ki: 0.00263–14.65 µM). These interactions involved specific bonds with amino acid residues, including conventional hydrogen, carbon-hydrogen, alkyl-alkyl, pi-alkyl, pi-sigma, pi-pi T-shaped, pi-anion, sulfur-x, or pi-pi stacked bonds between ARG110 and/or LYS318. These amino acids (residues 27–326) are located in the allosteric domain of PBP2a, facilitating the opening of the active site involved in nascent cell wall peptidoglycan synthesis [33]. This suggests that the binding of these molecules to the allosteric domain might induce a conformational change in PBP2a. This change disrupts the opening of the active site and inhibits cell wall peptidoglycan synthesis. Previous research has shown that (E)-3-(3-carboxyphenyl)-2-(4-cyanostyryl)quinazolin-4(3H)-one has been reported to bind at the allosteric domain of PBP2a, causing in a conformational change that inhibits MRSA growth [33]. Our findings support the idea that the seven compounds act as allosteric regulators of PBP2a, restoring MRSA’s sensitivity to amoxicillin. It has been reported that the dual combination of two β-lactam antibiotics, amoxicillin, and cefdinir, shows synergistic bactericidal efficacy against MRSA by inhibiting β-lactamase and PBPs, which enhances bacterial killing [15]. However, the specific mechanism of how the seven compounds inhibit PBP2a in combination with amoxicillin requires experimental verification.
In VRE, resistance is attributed to the VanA gene, which encodes VanA ligase. This enzyme modifies peptidoglycan synthesis by substituting D-alanine with D-lactate, reducing the effectiveness of vancomycin [2,4,6]. Our study demonstrated that seven compounds had strong binding with VanA ligase, showing high binding affinities and low predicted inhibition constants (ΔG: −10.46 to −7.08 kcal/mol; Ki: 0.021–4.82 µM). In contrast, amoxicillin showed weak binding to VanA ligase (ΔG: −6.59 kcal/mol; Ki: 14.66 µM). The compounds 1–7 interacted with VanA ligase at various amino acid residues (LYS73 to ARG317) via several types of interactions, including conventional hydrogen bonds, carbon-hydrogen, alkyl-alkyl, pi-alkyl, pi-sigma, pi-pi T-shaped, pi-anion, pi-pi stacked, pi-cation, and unfavorable donor-donor interactions. Notably, residues from positions 2–344 are involved in substrate binding during the transition from D-alanine-D-alanine to D- alanine-D-lactate [36]. These interactions, especially near or within the enzyme’s active site, disrupt the transition from D-alanine to D-lactate, which hinders the synthesis of D-alanine-D-lactate peptidoglycan precursors critical for vancomycin resistance. Therefore, these compounds might inhibit VanA ligase activity, which would reduce the transition from D-alanine to D-lactate and disrupt peptidoglycan synthesis. Furthermore, the synergistic effects of these phytochemicals with amoxicillin suggest that they were able to act on different target sites. The phytochemicals 1–7 directly inhibit VanA ligase activity, while amoxicillin binds to PBPs targets and also disrupts peptidoglycan synthesis in VRE. However, the molecular mechanisms of action for all compounds and amoxicillin should be confirmed in vitro, particularly regarding VanA ligase activity. Although this study shows promising results, there are several limitations that need to be addressed in future research. First, the findings are based on in silico molecular docking and in vitro testing, which should be confirmed with in vivo studies to verify the safety and effectiveness of these compounds in living organisms. The pharmacokinetics and toxicity of the phytochemicals were not tested, which is important for evaluating their potential as treatments. Future studies should focus on understanding how these compounds work in the body and their safety in clinical trials. Second, our study shows a synergistic effect between the phytochemicals and amoxicillin. Further research is needed to clarify the specific molecular mechanisms and to estimate potential in clinical study.
CONCLUSION
All compounds displayed antibacterial activity against MRSA and VRE for the first time, except compounds 1 and 7. Compound 3 was the most potent against both strains with MIC of 5 mg/ml. The combination of amoxicillin and seven phytochemicals has an additive effect on MRSA growth and a synergistic effect on VRE growth by checkerboard assay. MRSA strain and VRE strain were increasingly expressed resistance-related proteins: PBP2a and VanA ligase, respectively. The molecular docking study revealed the prediction of PBP2a/VanA ligase with seven phytochemicals to indicate the proposed mechanism of the phytochemicals 1–7 with amoxicillin against MRSA and VRE in Figure 4.
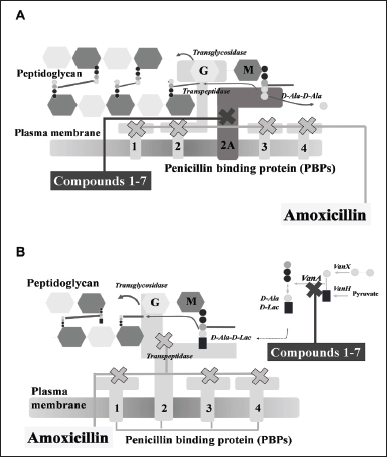 | Figure 4. The proposed mechanism of the seven phytochemical compounds {compound 1 (pinosylvin monomethyl ether), compound 2 (2,3’-dihydroxy-5’-methoxystilbene), compound 3 [(E)-2,3′-dihydroxy-2′-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-5′-methoxystilbene], compound 4 [(E)-2,5′-dihydroxy-2′-(4-hydroxybenzyl)-3′-methoxystilbene], compound 5 (isalpinin), compound 6 (oleanolic acid 28-O-β-D-glucopyranoside), compound 7 (piperine) and β-lactam amoxicillin} in combination with amoxicillin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (A) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis (B). [Click here to view] |
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors are thankful to the cell culture research laboratory of the Department of Medical Sciences, Faculty of Sciences, Rangsit University, for providing facilities.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
All authors made substantial contributions to conception and design, acquisition of data, or analysis and interpretation of data; took part in drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; agreed to submit to the current journal; gave final approval of the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work. All the authors are eligible to be an author as per the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) requirements/guidelines.
FINANCIAL SUPPORT
There is no funding to report.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors report no financial or any other conflicts of interest in this work.
ETHICAL APPROVALS
This study does not involve experiments on animals or human subjects.
DATA AVAILABILITY
All the data is available with the authors and shall be provided upon request.
PUBLISHER’S NOTE
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. This journal remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published institutional affiliation.
USE OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI)-ASSISTED TECHNOLOGY
The authors declares that they have not used artificial intelligence (AI)-tools for writing and editing of the manuscript, and no images were manipulated using AI.
REFERENCES
1. de Oliveira Santos JV, da Costa Júnior SD, de Fátima Ramos Dos Santos Medeiros SM, Cavalcanti IDL, de Souza JB, Coriolano DL, et al. Panorama of bacterial infections caused by epidemic resistant strains. Curr Microbiol. 2022;79(6):175. CrossRef
2. Janice J, Wagner TM, Olsen K, Hegstad J, Hegstad K. Emergence of vancomycin-resistant enterococci from vancomycin-susceptible enterococci in hospitalized patients under antimicrobial therapy. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2024;36:116–22. CrossRef
3. Ali Alghamdi B, Al-Johani I, Al-Shamrani JM, Musamed Alshamrani H, Al-Otaibi BG, Almazmomi K, et al. Antimicrobial resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2023;30(4):103604. CrossRef
4. Ahmed MO, Baptiste KE. Vancomycin-resistant Enterococci: a review of antimicrobial resistance mechanisms and perspectives of human and animal health. Microb Drug Resist. 2018;24(5):590–606. CrossRef
5. Vestergaard M, Frees D, Ingmer H. Antibiotic resistance and the MRSA problem. Microbiol Spectr. 2019;7(2):1–23. CrossRef
6. Quiñones D, Aung MS, Sousa Martins JP, Urushibara N, Kobayashi N. Genetic characteristics of VanA-type vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium in Cuba. New Microbes New Infect 2017;21:125–7. CrossRef
7. Lee AS, de Lencastre H, Garau J, Kluytmans J, Malhotra-Kumar S, Peschel A, et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:18033. CrossRef
8. Mahjabeen F, Saha U, Mostafa MN, Siddique F, Ahsan E, Fathma S, et al. An update on treatment options for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteremia: a systematic review. Cureus. 2022;14(11):e31486. CrossRef
9. Wingler MJ, Patel NR, King ST, Wagner JL, Barber KE, Stover KR. Linezolid for the treatment of urinary tract infections caused by vancomycin-resistant Enterococci. Pharmacy (Basel). 2021;9(4):175. CrossRef
10. Awadelkarim AM, Idris I, Abdelhai M, Yeddi A, Saad E, Alhusain R, et al. Daptomycin-associated diarrhea: a Case report and review of the literature. Cureus. 2022;14(6):e26135. CrossRef
11. Porchera BR, da Silva CM, Miranda RP, Gomes ARQ, Fernandes PHDS, de Menezes CGO, et al. Linezolid and vancomycin for nosocomial infections in pediatric patients: a systematic review. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2024;100(3):242–9. CrossRef
12. Husain A, Rawat V, Umesh, Kumar M, Verma PK. Vancomycin, linezolid and daptomycin susceptibility pattern among clinical isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from Sub-Himalyan Center. J Lab Physicians. 2018;10(2):145–8. CrossRef
13. Gentry CA, Rodvold KA, Novak RM, Hershow RC, Naderer OJ. Retrospective evaluation of therapies for Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. Pharmacotherapy. 1997;17(5):990–7.
14. Rybak MJ. The pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of vancomycin. Clin Infect Dis. 2006;42 Suppl 1:S35–9. CrossRef
15. Altarawneh H, Alhomra T, Alharbi M, Fan Y, Derrick JP, Xia G. Synergistic bactericidal activity of a novel dual β-lactam combination against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2024;79(7):1677–82. CrossRef
16. Descourouez JL, Jorgenson MR, Wergin JE, Rose WE. Fosfomycin synergy in vitro with amoxicillin, daptomycin, and linezolid against vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium from renal transplant patients with infected urinary stents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57(3):1518–20. CrossRef
17. Feng Y, Tonon CC, Hasan T. Dramatic destruction of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections with a simple combination of amoxicillin and light-activated methylene blue. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2022;235:112563. CrossRef
18. Barbieri R, Coppo E, Marchese A, Daglia M, Sobarzo-Sánchez E, Nabavi SF, et al. Phytochemicals for human disease: an update on plant-derived compounds antibacterial activity. Microbiol Res. 2017;196:44–68. CrossRef
19. Uzair B, Niaz N, Bano A, Khan BA, Zafar N, Iqbal M, et al. Essential oils showing in vitro anti MRSA and synergistic activity with penicillin group of antibiotics. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2017;30(5):1997–2002.
20. Schmidt S, Heimesaat MM, Fischer A, Bereswill S, Melzig MF. Saponins increase susceptibility of vancomycin-resistant enterococci to antibiotic compounds. Eur J Microbiol Immunol (Bp). 2014;4(4):204–12. CrossRef
21. Wu J, Li B, Xiao W, Hu J, Xie J, Yuan J, et al. Longistylin A, a natural stilbene isolated from the leaves of Cajanus cajan, exhibits significant anti-MRSA activity. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020;55(1):105821. CrossRef
22. Plumed-Ferrer C, Väkeväinen K, Komulainen H, Rautiainen M, Smeds A, Raitanen JE, et al. The antimicrobial effects of wood-associated polyphenols on food pathogens and spoilage organisms. Int J Food Microbiol. 2013;164(1):99–107. CrossRef
23. Chan BCL, Ip M, Gong H, Lui SL, See RH, Jolivalt C, et al. Synergistic effects of diosmetin with erythromycin against ABC transporter over-expressed methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) RN4220/pUL5054 and inhibition of MRSA pyruvate kinase. 2013;20(7):611–4. CrossRef
24. Wang SY, Sun ZL, Liu T, Gibbons S, Zhang WJ, Qing M. Flavonoids from Sophora moorcroftiana and their synergistic antibacterial effects on MRSA. Phytother Res. 2014;28:1071–6. CrossRef
25. Lertnitikul N, Liangsakul J, Jianmongkol S, Suttisri R. Three new cytotoxic stilbene dimers from Paphiopedilum dianthum. Nat Prod Res. 2023;37(21):3685–93. CrossRef
26. Khameneh B, Iranshahy M, Ghandadi M, Atashbeyk DG, Bazzaz BSF, Iranshahi M. Investigation of the antibacterial activity and efflux pump inhibitory effect of co-loaded piperine and gentamicin nanoliposomes in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. 2014;41(6):989–94. CrossRef
27. Lertnitikul N, Suttisri R, Sitthigool S, Pattamadilok C, Piewpong K, Khanboon A, et al. Antioxidant, antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities of amides and aristolactams from Piper wallichii (Miq.) Hand.-Mazz. Stems JBAPN. 2023;13(2):94–104. CrossRef
28. Powthong P, Suntornthiticharoen P. Comparative analysis of antioxidant, antimicrobial, and tyrosinase inhibitory activities of Centella asiatica (l.) Urb and Eichhornia crassipes (mart.) Solms. JMPAS. 2023;12-I14:5931–8. CrossRef
29. CLSI. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing M100. 31st ed. Wayne: PA: Clinical and laboratory standards institute; 2021.
30. Kuok CF, Hoi SO, Hoi CF, Chan CH, Fong IH, Ngok CK, et al. Synergistic antibacterial effects of herbal extracts and antibiotics on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a computational and experimental study. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017;242(7):731–43. CrossRef
31. Boonyong C, Jianmongkol S. Predicting molecular mechanism of silymarin-potentiated diclofenac toxicity: insight from in silico molecular docking. Toxicol Rep. 2023;11:339–45. CrossRef
32. Boonyong C, Lertnitikul N, Pattamadilok C, Sitthigool S, Suttisri R, Jianmongkol S, et al. In vitro and in silico effects of the polyisoprenylated benzophenones guttiferone K and oblongifolin C on P-glycoprotein function. J Appl Pharm Sci. 2024;14(02):102–8. CrossRef
33. Bouley R, Kumarasiri M, Peng Z, Otero LH, Song W, Suckow MA, et al. Discovery of antibiotic (E)-3-(3-carboxyphenyl)-2-(4-cyanostyryl)quinazolin-4(3H)-one. J Am Chem Soc. 2015;137(5):1738–41. CrossRef
34. Bakrim S, Machate H, Benali T, Sahib N, Jaouadi I, Omari NE, et al. Natural sources and pharmacological properties of pinosylvin. Plants (Basel). 2022;11(12):1541. CrossRef
35. Mattio LM, Catinella G, Dallavalle S, Pinto A. Stilbenoids: a natural arsenal against bacterial pathogens. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020;9(6):336. CrossRef
36. Roper DI, Huyton T, Vagin A, Dodson G. The molecular basis of vancomycin resistance in clinically relevant Enterococci: crystal structure of D-alanyl-D-lactate ligase (VanA). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(16):8921–5. CrossRef